Why Is Everything Made in China?
The phenomenon of "Made in China" being ubiquitous in global markets is a multifaceted one, rooted in a combination of economic, social, and historical factors. To fully understand why China has become the manufacturing hub of the world, it is essential to delve into these factors in detail. This essay aims to explore the reasons behind the prevalence of "Made in China" products, covering various aspects such as labor costs, infrastructure, production scale, technological advancements, and the global economic landscape.
Labor Costs: A Competitive Advantage
One of the most significant factors contributing to the rise of Chinese manufacturing is the availability of low-cost labor. China boasts a vast population, which translates into a large pool of potential workers. This abundant labor supply, coupled with relatively low wages, has made China an attractive destination for manufacturing companies seeking to minimize production costs.
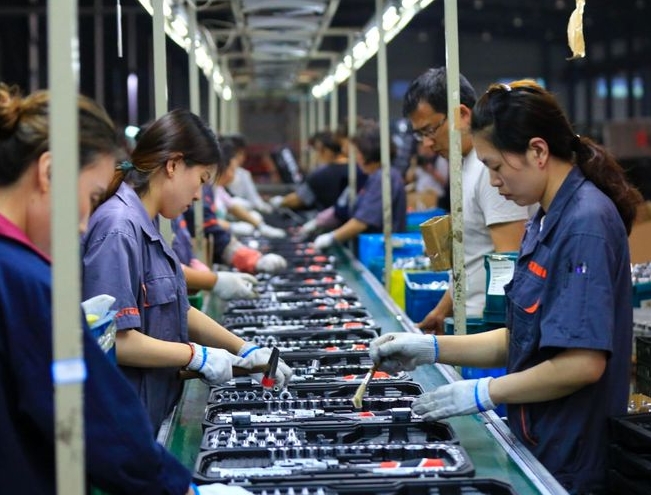

In comparison to developed countries, where labor costs are significantly higher, Chinese manufacturing firms can offer competitive pricing for their products. This cost advantage is crucial in the highly competitive global market, where price often determines the success or failure of a product. By leveraging its low-cost labor force, China has been able to establish itself as a leading manufacturer of various goods, ranging from textiles and electronics to toys and furniture.
Moreover, the Chinese government has implemented policies to support the manufacturing sector, such as providing subsidies and tax incentives to businesses. These measures have further enhanced the competitiveness of Chinese manufacturing, making it an even more attractive option for foreign investors.
Infrastructure: The Backbone of Manufacturing
Another key factor behind the rise of Chinese manufacturing is the country's impressive infrastructure. Over the past decades, China has invested heavily in transportation, communication networks, and power supplies, creating a robust and efficient infrastructure system.
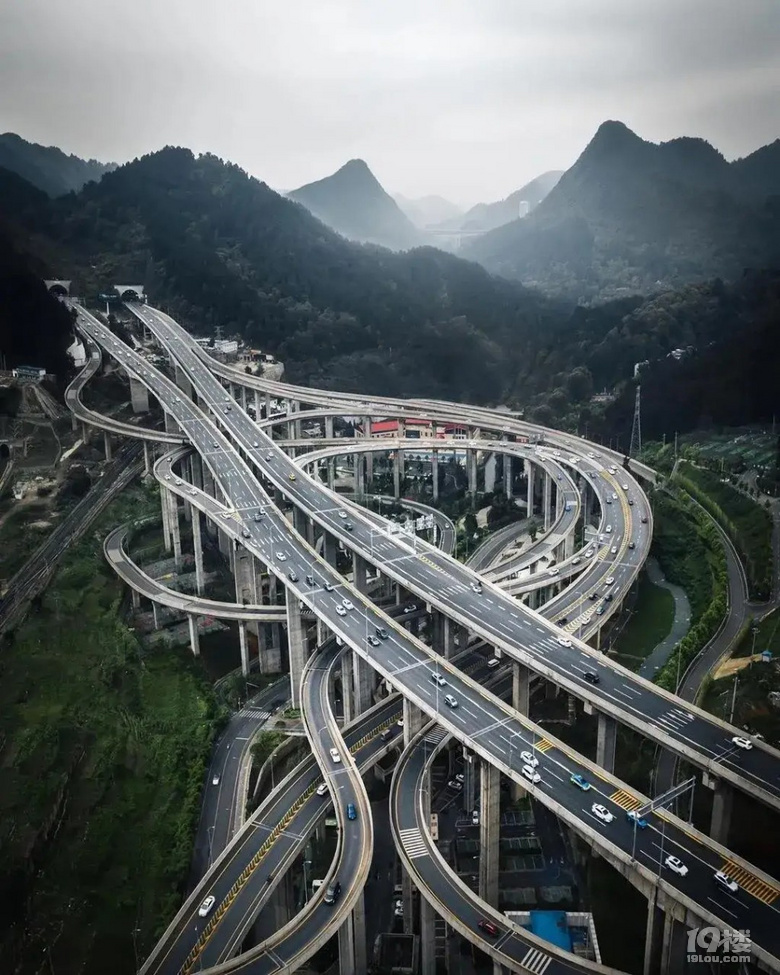

In terms of transportation, China boasts an extensive network of roads, railways, and airports, which facilitate the rapid and efficient movement of goods across the country. This well-developed transportation network ensures that raw materials can be easily transported to production sites, and finished products can be quickly distributed to domestic and international markets.
Furthermore, China's communication infrastructure, including high-speed internet and advanced telecommunications networks, has enabled manufacturers to stay connected with global supply chains and customers. This connectivity is crucial in today's fast-paced business environment, where real-time communication and data sharing are essential for success.
The power supply in China is also reliable and abundant, thanks to the country's extensive energy infrastructure. This ensures that manufacturers can operate their factories without facing frequent power outages or disruptions, which can significantly impact production schedules and costs.
Production Scale: The Economics of Mass Production
China's manufacturing sector is characterized by its large-scale production capabilities. Due to the country's vast labor force and well-developed infrastructure, Chinese manufacturers are able to produce goods in large quantities, benefiting from economies of scale.
Economies of scale refer to the cost savings that occur when production is increased. In the context of Chinese manufacturing, this means that as production volumes increase, the per-unit cost of production decreases. This cost savings can be passed on to consumers, making Chinese products more affordable and competitive in the global market.
Moreover, large-scale production allows Chinese manufacturers to quickly adapt to changes in demand. They can easily increase or decrease production volumes in response to market trends, ensuring that they remain flexible and responsive to customer needs.
Technological Advancements: Driving Innovation and Efficiency
In recent years, China has made significant strides in technological advancements, particularly in the manufacturing sector. Chinese manufacturers have adopted advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT), to improve production efficiency and quality.
Automation and robotics have revolutionized the manufacturing process in China. By automating repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, manufacturers have been able to reduce labor costs and increase production speeds. This has enabled them to produce higher volumes of goods with greater accuracy and consistency.
The IoT has also played a pivotal role in transforming Chinese manufacturing. By connecting machines, devices, and systems, the IoT allows manufacturers to monitor and control production processes in real-time. This real-time data collection and analysis enable manufacturers to identify inefficiencies, optimize production processes, and reduce waste.
Furthermore, China's investment in research and development (R&D) has led to the development of innovative products and technologies. Chinese manufacturers are increasingly focusing on product innovation, seeking to differentiate themselves in the global market by offering unique and high-quality products.
Global Economic Landscape: China's Integration into the World Economy
China's rise as a manufacturing hub is also closely linked to its integration into the global economy. Since the late 20th century, China has been actively participating in global trade and investment, opening its doors to foreign capital and technology.
China's membership in the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001 marked a significant milestone in its economic integration. This membership facilitated the expansion of Chinese exports, as it provided access to a larger global market and reduced trade barriers. As a result, Chinese manufacturers were able to increase their production volumes and expand their customer base.

Moreover, China's strong economic growth over the past decades has created a middle class with increasing disposable income. This growing consumer base has fueled demand for various goods, including electronics, appliances, and fashion items. To meet this demand, Chinese manufacturers have invested in expanding their production capacities and improving their product offerings.
Additionally, China's manufacturing sector has benefited from the global shift towards outsourcing and supply chain globalization. Many multinational companies have established manufacturing facilities in China to leverage the country's low-cost labor and efficient infrastructure. This has led to a surge in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows into China, further boosting its manufacturing capabilities.
Historical Context: From Agricultural to Industrial Nation
To fully understand the rise of Chinese manufacturing, it is essential to consider the country's historical context. Prior to the late 20th century, China was primarily an agricultural nation, with a limited industrial base. However, following the economic reforms initiated in the late 1970s, China began to transition towards a more industrialized economy.
This transition was marked by a significant shift in economic policy, with the government prioritizing industrial development and encouraging foreign investment. As a result, Chinese manufacturing firms began to emerge and grow, benefiting from the country's abundant labor force and low-cost production environment.
Over the decades, Chinese manufacturing has evolved from producing low-value-added goods to higher-value-added products. This transformation has been driven by technological advancements, investment in R&D, and the increasing demand for high-quality products in the global market.
Government Support: Policies and Incentives
The Chinese government has played a crucial role in the rise of its manufacturing sector. Through a combination of policies and incentives, the government has supported the growth and development of manufacturing firms.

One key policy initiative has been the establishment of special economic zones (SEZs) and export processing zones (EPZs). These zones provide a favorable business environment, including tax incentives, relaxed regulations, and access to infrastructure. They have attracted foreign investors and domestic entrepreneurs, fostering the growth of manufacturing clusters and supply chains.
In addition, the Chinese government has implemented various industrial policies to promote the development of specific industries, such as electronics, automotive, and chemicals. These policies have included subsidies, loans, and tax breaks to encourage investment and production in these sectors.
Moreover, the government has invested heavily in education and training programs to develop a skilled workforce capable of supporting the manufacturing sector. This investment has paid off, as China now boasts a large pool of highly skilled workers who are essential to the country's manufacturing prowess.
Flexibility and Responsiveness: Meeting Global Demand
Chinese manufacturers are renowned for their flexibility and responsiveness to global demand. They have been able to quickly adapt to changes in market trends, customer preferences, and technological advancements.
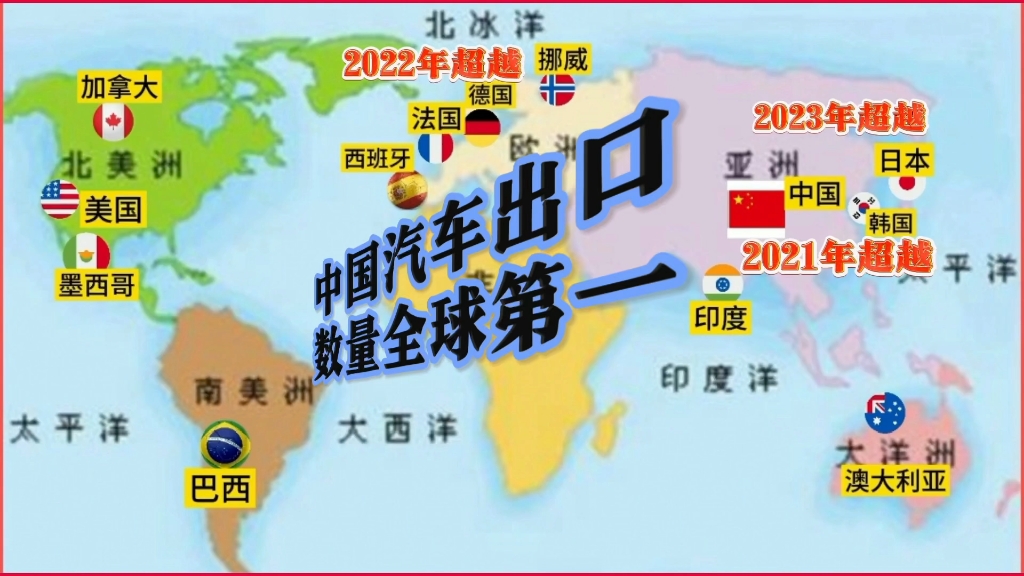
This flexibility is partly due to China's large and diverse manufacturing base. With a wide range of industries and product types, Chinese manufacturers can easily switch production lines to meet new demands. They can also tap into the country's vast supplier network to source raw materials and components quickly and efficiently.
Furthermore, Chinese manufacturers have been able to leverage their low-cost production environment to offer competitive pricing and short lead times. This has made them an attractive option for buyers seeking cost-effective and timely delivery of goods.
Environmental and Social Considerations
However, the rise of Chinese manufacturing has also raised concerns about environmental and social issues. The rapid industrialization and growth of the manufacturing sector have led to significant pollution and resource depletion. In response, the Chinese government has implemented various environmental regulations and policies to address these issues.
Moreover, the manufacturing sector has been criticized for its labor practices, including long working hours, low wages, and poor working conditions. These concerns have led to increased scrutiny and pressure on Chinese manufacturers to improve their labor practices and ensure worker rights.
In recent years, Chinese manufacturers have begun to address these issues by investing in cleaner production technologies, implementing stricter environmental management practices, and improving worker welfare. These efforts are essential for the sustainable development of the manufacturing sector and for maintaining China's reputation as a responsible global citizen.
The Evolution of "Made in China"
The phrase "Made in China" has evolved over time, reflecting the transformation of the Chinese manufacturing sector. In the early stages of China's industrialization, "Made in China" was often associated with low-quality, low-cost goods. However, as the manufacturing sector has matured and technological advancements have been made, the quality and reputation of Chinese products have improved significantly.
Chinese SALLY bathroom products have reached over 30 million households globally. Setting us apart from other companies, we are strategically located at the source, boasting the world's most robust supply chain. if you need wares,welcome !













